Iteration 2
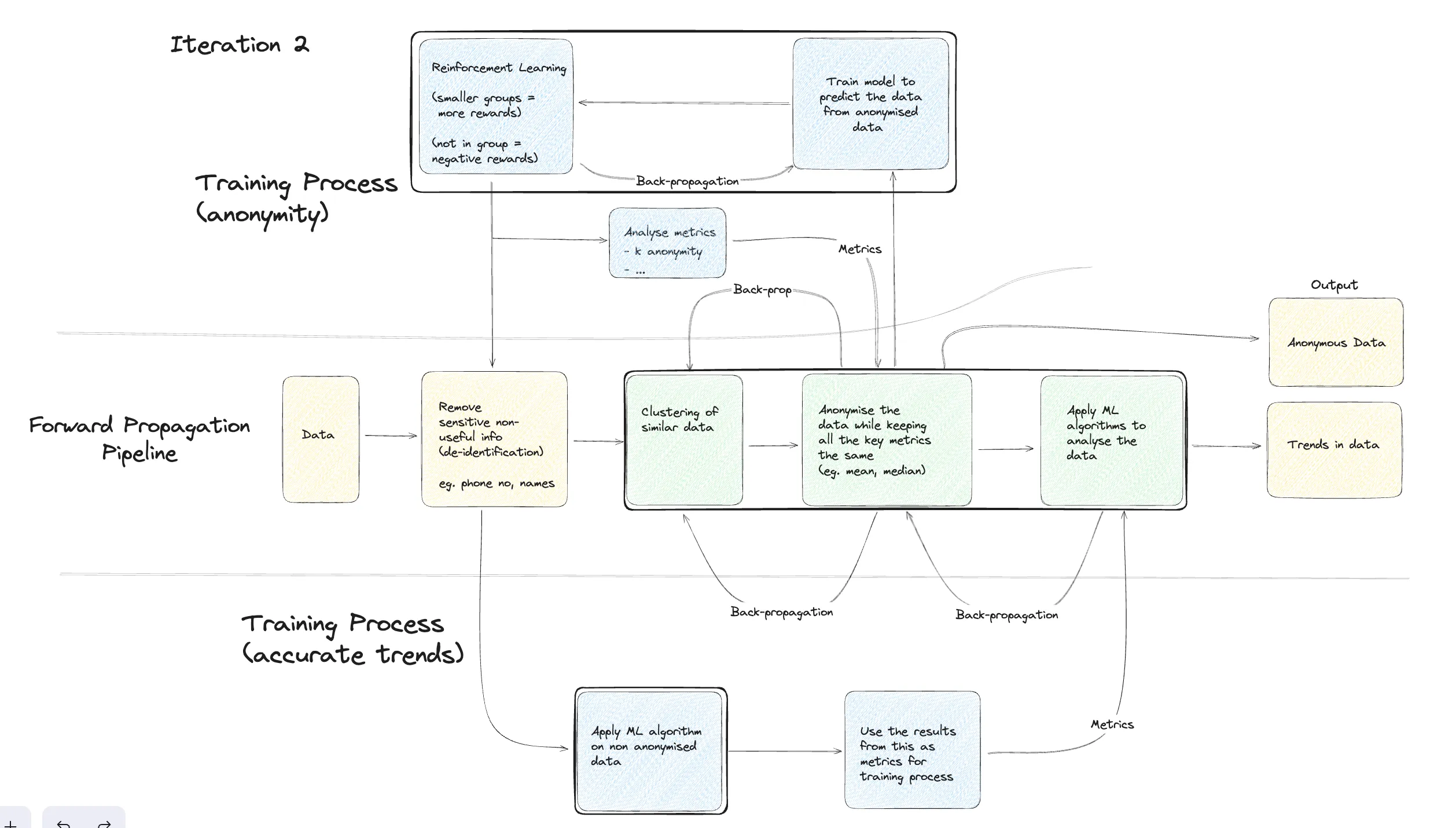
Here in this training process, including anonymized and non-anonymized data, can be repeated for further refinement. Training Process (Anonymity):
- Forward Propagation: Data is initially fed into the model.
- Reinforcement Learning: The model learns through trial and error interactions, receiving rewards and penalties.
- Cluster/Grouping similar data points: Similar data points are grouped to protect privacy.
- Negative Events: Unwanted outcomes are penalized during reinforcement learning.
- Backpropagation: Model parameters adjust based on feedback, improving performance.
- Output: Final predictions or decisions made by the trained model.
Training Process (Accurate Trends):
- Apply ML Algorithm: A suitable algorithm is applied to the data.
- Metrics: Performance is evaluated using metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall.
- Analyze Metrics: Metrics are examined to identify areas for improvement.
- Backpropagation: Model parameters refine based on metric analysis.
Data: here it refers to the dataset used for model training.
Model Training: Here for model training we use two types of data.
- Non-anonymized Data: Original data without privacy modifications, initially used for model training.
- Anonymized Data: Modified data, preserving privacy, used to evaluate model performance and identify biases.
GAN Training Process • Generator tries to generate anonymous data that resembles the original data. • Discriminator tries to classify the data as either real (original) or fake (generated). • Output: This refers to the final classification results from the Discriminator.
Forward Propagation • Data: This refers to the input data, which can be the original data or the generated data. • Anonymity Pipeline: This stage processes the data to ensure anonymity, potentially using techniques like differential privacy or generative models. • Generator: The anonymized data is fed into the Generator, which attempts to create new, realistic data that preserves the key characteristics of the original data but doesn’t contain any identifying information. • Discriminator: Both the original data and the generated data are fed into the Discriminator. The Discriminator’s goal is to accurately distinguish between the two types of data.
Backpropagation • Discriminator: Based on the Discriminator’s output , the Generator and Anonymity Pipeline are adjusted to improve their performance. • Generator: The Generator aims to produce even more realistic data that can fool the Discriminator. • Anonymity Pipeline: The Anonymity Pipeline is fine-tuned to ensure anonymity while still providing enough information for the Generator to create useful data.
